When I first started in storage technology (it doesn’t seem like that long ago, really!) the topic seemed like it was becoming rather stagnant. The only thing that seemed to be happening was that disks were getting bigger (more space) and the connections were getting faster (more speed).
More speed, more space; more space, more speed. Who doesn’t like that? After all, you can never have too much bandwidth, or too much disk space! Even so, it does get rather routine. It gets boring. It gets well, “what have you done for me lately?”
Then came Flash.
People said that Flash memory was a game changer, and though I believed it, I just didn’t understand how, really. I mean, sure, it’s really, really fast storage drives, but isn’t that just the same story as before? This is coming, of course, from someone who was far more familiar with storage networks than storage devices.
Fortunately, I kept that question to myself (well, at least until I was asked to write this blog), thus saving myself from potential embarrassment.
There is no shortage of Flash vendors out there who (rightfully) would have jumped at the chance to set my misinformed self on the straight and narrow; they would have been correct, too. Flash isn’t just “cool,” it allows the coordination, access, and retrieval of data in ways that simply weren’t possible with more traditional media.
There are different ways to use Flash, of course, and different architectures abound in the marketplace – from fully “All Flash Arrays” (AFA), “Hybrid Arrays” (which are a combination of Flash and spinning disk), to more traditional systems that have simply replaced the spinning drives with Flash drives (without much change to the architecture).
Even through these architectures, though, Flash is still constrained by the very basic tenets of SCSI connectivity. While this type of connectivity works very well (and has a long and illustrious history), the characteristics of Flash memory allow for some capabilities that SCSI wasn’t built to do.
Enter NVMe.
What’s NVMe?
Glad you asked. NVMe stands for “Non-Volatile Memory Express.” If that doesn’t clear things up, let’s unpack this a bit.
Flash and Solid State Devices (SSDs) are a type of non-volatile memory (NVM). At the risk of oversimplifying, NVM is a type of memory that keeps its content when the power goes out. It also implies a way by which the data stored on the device is accessed. NVMe is a way that you can access that memory.
If it’s not quite clear yet, don’t worry. Let’s break it down with pretty pictures.
Starting Before the Beginning – SCSI
For this, you better brace yourself. This is going to get weird, but I promise that it will make sense when it’s all over.
Let’s imagine for the moment that you are responsible for programming a robot in a factory. The factory has a series of conveyor belts, each with things that you have to put and get with the robot.

The robot is on a track, and can only move from sideways on the track. Whenever it needs to get a little box on the conveyor belt, it has to move from side to side until it gets to the correct belt, and then wait for the correct orange block (below) to arrive as the belt rotates.
Now, to make things just a little bit more complicated, each conveyor belt is a little slower than the previous one. For example, belt 1 is the fastest, belt 2 is a little slower, belt 3 even slower, and so on.
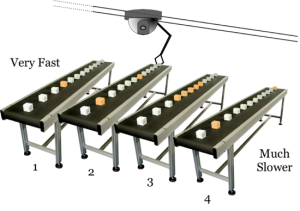
In a nutshell, this is analogous to how spinning disk drives work. The robot arm – called a read/write head – moves across a spinning disk from sector to sector (analogous, imperfect as it may be, to our trusty conveyor belts) to pick up blocks of data.
(As an aside, this is the reason why there are differences in performance between long contiguous blocks to read and write – called sequential data – and randomly placing blocks down willy-nilly in various sectors/conveyor belts – called random read/writes.)
Now remember, our trusty robot needs to be programmed. That is, you – in the control room – need to send instructions to the robot so that it can get/put its data. The command set that is used to do this, in our analogy, is SCSI.
Characteristics of SCSI
SCSI is a tried-and-true command structure. It is, after all, the protocol for controlling most devices in the world. In fact, its ubiquity is so prevalent, most people nowadays think that it’s simply a given. It works on so many levels and layers as an upper layer protocol, with so many different devices, that it’s easily the default “go-to” application. It’s used with Fibre Channel, FCoE, iSCSI (obviously), InfiniBand – even the hard drives in your desktop and laptops.
It was also built for devices that relied heavily on the limitations of these conveyor belts. Rotational media has long been shown as superior than linear (i.e., tape) in terms of speed and performance, but the engineering required to make up for the changes in speeds from the inside of the drive (where the rotational speed is much slower) to the outside – similar to the difference between our conveyor belts “4” and “1” – results in some pretty fancy footwork on the storage side.
Because the robot arm must move back and forth, it’s okay that it can only handle one series of commands at a time. Even if you could tell it to get a block from conveyor belt 1 and 3 at the same time, it couldn’t do it. It would have to queue the commands and get to each in turn.
So, the fact that SCSI only sent commands one-at-a-time was okay, because the robot could only do that anyway.
Then came Flash, and suddenly the things seemed a bit… constricted.
The Flash Robot
Let’s continue with the analogy, shall we? We still have our mandate – control a robot to get and put blocks of information onto storage media. This time, it’s Flash.
First, let’s do away with the conveyor belts altogether. Instead, let’s lay out all the blocks (in a nice OCD-friendly way) on the media, so that the robot arm can see it all at once:
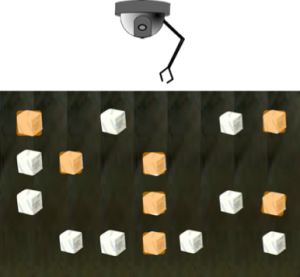
From its omniscient view, the robot can “see” all the blocks at once. Nothing moves, of course, as this is solid-state. However, as it stands, this is how we currently use Flash with a robot arm that responds to SCSI commands. We still have to address our needs one-at-a-time.
Now, it’s important to note that because we’re not talking about spinning media, the robot arm can go really fast (of course, there’s no real moving read/write head in a Flash drive, but remember we’re looking at this from a SCSI standpoint). The long and the short of it is that even though we can see all of the data from our vantage point, we still only ask for information one at a time, and we still only have one queue for those requests.
Enter NVMe
This is where things get very interesting.
NVMe is the standardized interface for PCIe SSDs (it’s important to note, however, that NVMe is not PCIe!). It was architected from the ground-up, specifically for the characteristics of Flash and NVM technologies.
Most of the technical specifics are available at the NVM Express website, but here are a couple of the main highlights.
First, whereas SCSI has one queue for commands, NVMe is designed to have up to 64 thousand queues. Moreover, each of those queues in turn can have up to 64 thousand commands. Simultaneously. Concurrently. That is, at the same time.
That’s a lot of freakin’ commands goin’ on at once!
Let’s take a look at our programmable robot. To complete the analogy, instead of one arm, our intrepid robot has 64 thousand arms, each with the ability to handle 64 thousand commands.
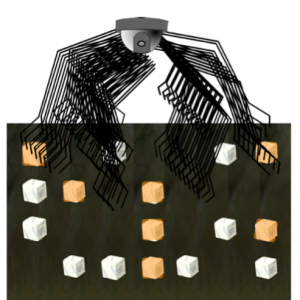
Second, NVMe streamlines those commands to only the basics that Flash technologies need: 13 to be exact.
Remember when I said that Flash has certain characteristics that allow for radically changing the way data centers store and retrieve data? This is why.
Flash is already fast. NVMe can make this even faster than we do so today. How fast? Very fast.
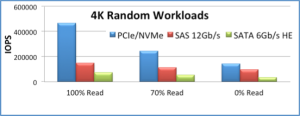
Source: The Performance Impact of NVMe and NVMe over Fabrics
This is just an example, of course, because enterprise data centers have more workloads than just those that run 4K random reads. Even so, it’s a pretty nifty example:
- For 100% random reads, NVMe has 3x better IOPS than 12Gbps SAS
- For 70% random reads, NVMe has 2x better IOPS than 12Gbps SAS
- For 100% random writes, NVMe has 1.5x better IOPs than 12Gbps SAS
What about sequential data?
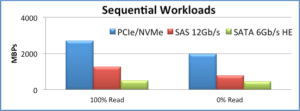
Source: The Performance Impact of NVMe and NVMe over Fabrics
Again, this is just one scenario, but the results are still quite impressive. For one, NVMe delivers greater than 2.5Gbps read performance and ~2Gbps write performance:
- 100% reads: NVMe has 2x performance of 12Gbps SAS
- 100% writes: NVMe has 2.5x performance of 12Gbps SAS
Of course, there is more to data center life than IOPS! Those efficiencies of command structure that I mentioned above also reduce CPU cycles by half, as well as reduce latency by more than 200 microseconds than 12 Gbps SAS.
I know it sounds like I’m picking on poor 12 Gbps SAS, but at the moment it is the closest thing to the NVMe-type of architecture. The reason for this is because of NVMe’s relationship with PCIe.
Relationship with PCIe
If there’s one place where there is likely to be some confusion, it’s here. I have to confess, when I first started going deep into NVMe, I got somewhat confused, too. I understood what PCIe was, but I was having a much harder time figuring out where NVMe and PCIe intersected, because most of the time the conversations tend to blend the two technologies together in the discussion.
That’s when I got it: they don’t intersect.
When it comes to “hot data,” we in the industry have been seeing a progressive migration towards the CPU. Traditional hosts contain an I/O controller that sits in-between the CPU and the storage device. By using PCIe, however it is possible to eliminate that I/O controller from the data path, making the flows go very, very quick.
Because of the direct connection to the CPU, PCIe has some pretty nifty advantages, including (among others):
- Lower latency
- Scalable performance (1 GB/s, per lane, and PCI 3.0 x8 cards have 8 lanes – that’s what the “x8” means)
- Increased I/O (up to 40 PCIe lanes per CPU socket)
- Low power
This performance of PCIe, as shown above, is significant. Placing a SSD on that PCIe interface was, and is, inevitable. However, there needed to be a standard way to communicate with the SSDs through the PCIe interface, or else there would be a free-for-all for implementations. The interoperability matrices would be a nightmare!
Enter NVMe.
NVM Express is that standardized way of communicating with a NVM storage device, and is backed by an ever-expanding consortium of hardware and software vendors to make your life easier and more productive with Flash technologies.
Think of PCIe as the physical interface and NVMe as the protocol for managing NVM devices using that interface.
Not Just PCIe, Fabrics!
Just like with SCSI, an interest has emerged in moving the storage outside of the host chassis itself. It’s possible to do this with PCIe, but it requires extending the PCIe hardware interface outside as well, and as a result there has been some interest in using NVMe with other interface and storage networking technologies.
Work is progressing on not just point-to-point communication (PCIe, RDMA-friendly technologies such as RoCE and iWARP), but also Fabrics as well (InfiniBand-, Ethernet- and Fibre Channel-based, including FCoE).
By expanding these capabilities, it will be possible to attach hundreds, maybe thousands, of SSDs in a network – far more than can be accommodated via PCIe-based systems. There are some interesting aspects for NVMe using Fabrics that are best left for another blog post, but it was worth mentioning here as an interesting tidbit.
Bottom Line
NVM Express has been in development since 2007, believe it or not, and has just released version 1.2 as of this writing. Working prototypes of NVMe using PCIe- and Ethernet-based connectivity have been demonstrated for several years. It’s probably the most-developed standards work that few people have ever heard about!
Want to learn more? I encourage you to listen/watch the SNIA ESF Webcast “The Performance Impact of NVMe and NVMe over Fabrics” which goes into much more technical detail, sponsored by the NVMe Promoter’s Board and starring some of the brainiacs behind the technical work. Oh, and I’m there too (as the moderator, of course).
Keep an eye open for more information about NVMe in the coming months. The progress made is remarkably rapid, and more companies are joining each year. It will be extremely interesting to see just how creative the data center architectures can get in the coming years, as Flash technology comes to realize its full potential.
Update: Want to learn more about NVMe? Check out these SNIA ESF webcasts:





